Linear Regulator
A linear regulator is an electronic circuit that maintains a constant output voltage despite variations in input voltage, load current, or temperature. It operates by dissipating excess voltage as heat, hence the term "linear."
In short, it is a component that takes a variable input voltage and produces a stable, predetermined output voltage.

Schematic of an Adjustable Voltage Regulator Using LM317:
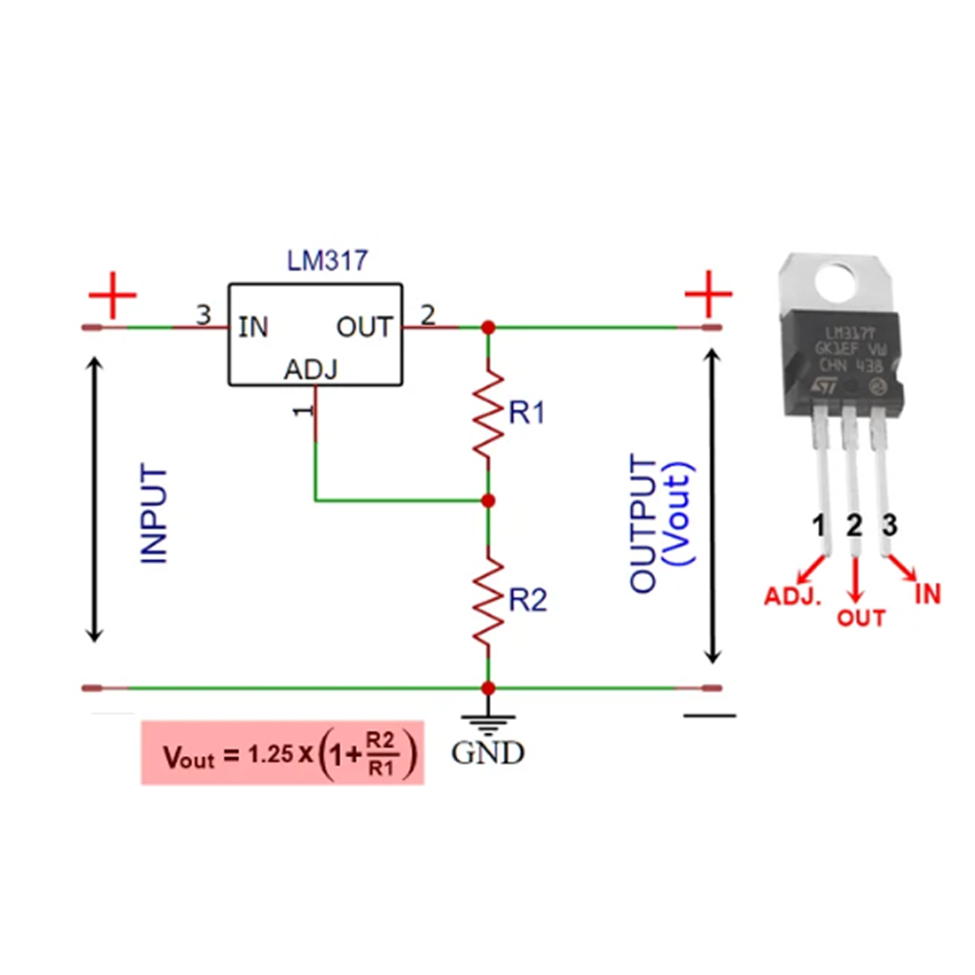

Key Points:
- Constant output voltage: This is its primary function. It ensures that the powered device receives the stable voltage required for proper operation.
- Heat dissipation: The excess voltage (the difference between the input and output voltage) multiplied by the load current is dissipated as heat. This is the main limitation of linear regulators, as it reduces their efficiency and often requires heat sinks.
- Simplicity and low noise: Linear regulators are generally simple to implement and produce an output voltage with very little electronic noise.
Examples of Common Linear Regulators:
-
LDO (Low Dropout Regulator):
- A type of linear regulator optimized to operate with a small voltage difference between input and output (the "dropout voltage").
- More efficient than standard linear regulators when the input voltage is only slightly higher than the desired output voltage.
- Widely used in battery-powered applications.
-
LM317:
- An adjustable linear voltage regulator.
- Its output voltage can be set using two external resistors.
- Capable of providing a wide range of output voltages and a reasonable current output.
-
78xx Series:
- Fixed positive linear voltage regulators.
- The "xx" indicates the fixed output voltage (e.g., the 7805 provides +5V, the 7812 provides +12V).
- Simple to use and widely available for obtaining regulated positive voltages.
- The complementary 79xx series provides regulated negative voltages (e.g., the 7905 for -5V).
See other components: