Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive electronic component used to store electrical energy in an electric field. It acts as an electricity reservoir and consists of two conductive plates (called electrodes) separated by an insulating material (called a dielectric). When a voltage is applied across the two plates, opposite electric charges accumulate on each, creating an electric field.
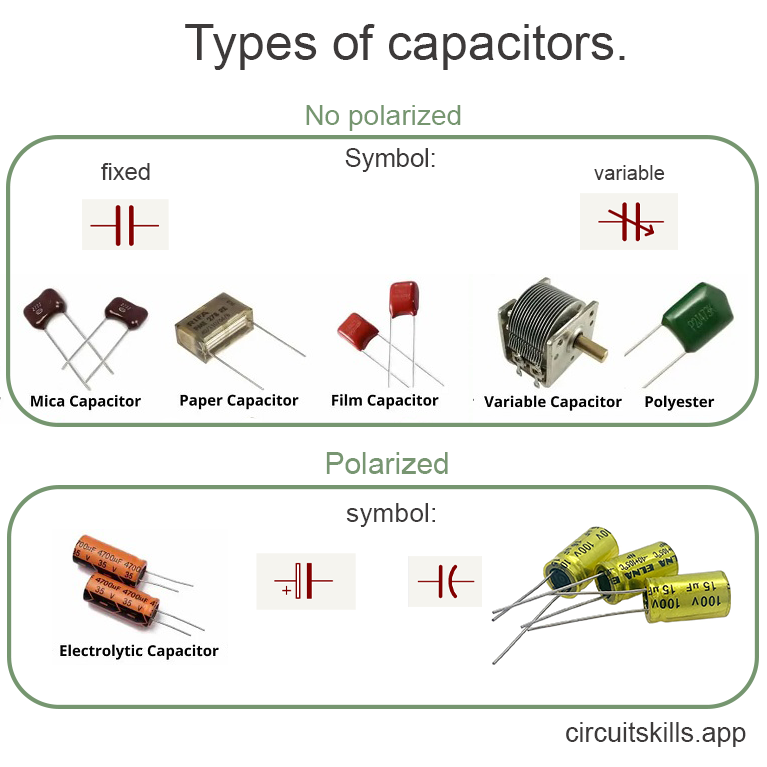
There are various types of capacitors, differing in composition and operation. Observe the different types along with their corresponding symbols.
Operation:
Charging: When a voltage is applied, electrons accumulate on one plate, creating a negative charge, while the other plate loses electrons, creating a positive charge.
Discharging: When the voltage is removed, the capacitor can release the stored energy.
Key Characteristics:
Capacitance (C): Measured in farads (F), it indicates the amount of charge the capacitor can store for a given voltage. Capacitance depends on the surface area of the plates, the distance between them, and the nature of the dielectric.
Rated Voltage: The maximum voltage the capacitor can withstand without risk of breakdown (dielectric failure).
Applications:
- Filtering: In power supplies to smooth voltage.
- Energy Storage: In electronic circuits to provide instant power.
- Coupling & Decoupling: To block direct current (DC) while allowing alternating current (AC) to pass.
- Timing: In timing circuits (such as oscillators).
Types:
Polarized:
Electrolytic Capacitor
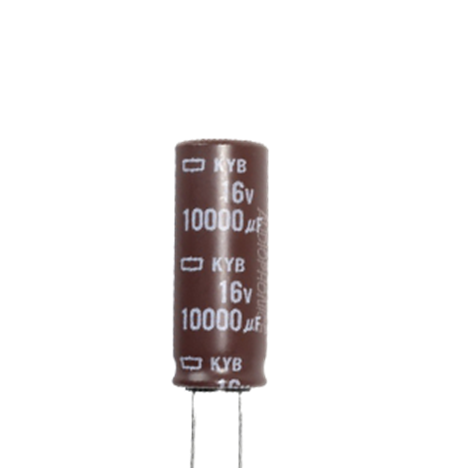

An electrolytic capacitor is a type of polarized capacitor that uses an electrolyte (liquid or solid) as one of its electrodes to achieve high capacitance in a compact size. It is one of the most commonly used capacitors in electronics, especially in circuits requiring large capacitance values. They offer high capacitance (ranging from microfarads (µF) to farads (F)) but have a limited rated voltage.
Applications:
Power supply filtering: To smooth DC voltage after rectification (e.g., C1).
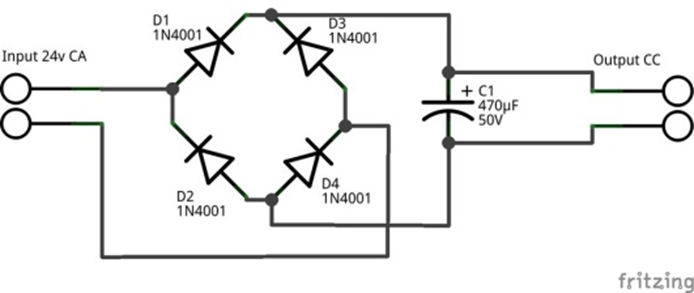 DC coupling: In audio circuits to block DC while allowing AC signals to pass.
DC coupling: In audio circuits to block DC while allowing AC signals to pass.
Energy storage: In circuits requiring high capacitance.
Caution:
Polarity reversal: Reversing polarity can severely damage the capacitor, cause electrolyte leakage, or even lead to an explosion.
Lifespan: Electrolytic capacitors have a limited lifespan, especially when exposed to high temperatures.
Non-Polarized:
1.Ceramic Capacitor
- The dielectric is made of ceramic, a non-conductive material.
- They are typically small and inexpensive.
Characteristics:
- Non-polarized: Can be connected in any direction.
- Low capacitance: Typically in the picofarad (pF) to microfarad (µF) range.
- High-frequency performance: Excellent for high frequencies due to low inductance.
- Thermal stability: Relatively stable performance across temperature ranges.
Applications:
- Decoupling in digital circuits.
- High-frequency filtering.
- RF (radio frequency) circuits.
Drawbacks: - Low capacitance compared to electrolytic capacitors.
- Sensitive to voltage variations (piezoelectric effect).
2. Film Capacitor
Description:
The dielectric is a plastic film (polyester, polypropylene, polycarbonate, etc.).
The electrodes are often metal deposited on the film.
Characteristics:
- Non-polarized: Can be used in AC or DC circuits.
- Moderate capacitance: Ranging from nanofarads (nF) to microfarads (µF).
- Low losses: Excellent stability and low energy dissipation.
- Long lifespan: Highly reliable and durable.
Applications: - Audio filtering (high sound quality).
- Coupling and decoupling in analog circuits.
- Power circuits (polypropylene for high voltage).
Drawbacks: - Bulkier than ceramic capacitors for similar capacitance values.
- More expensive than ceramic capacitors.
3. Variable Capacitor
- Description:
- These capacitors have adjustable capacitance, either manually or electronically.
- They often consist of movable metal plates (rotor) and fixed plates (stator) separated by a dielectric (air, ceramic, etc.).
- Characteristics:
- Adjustable capacitance: Varies based on plate positioning.
- Capacitance range: Typically from a few picofarads (pF) to a few hundred pF.
- Non-polarized: Can be used in AC or DC circuits.
- Applications:
- Frequency tuning in radios (old crystal or transistor radios).
- RF tuning circuits in electronics.
- Drawbacks:
- Mechanically fragile (for manual models).
- Limited capacitance compared to other types.
Value Decoding
Ceramic Capacitors:
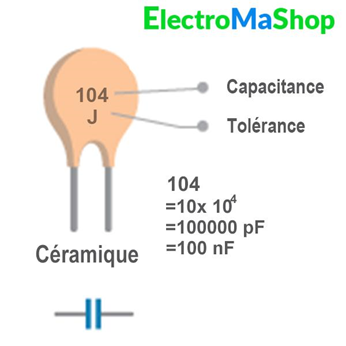 Value decoding → use a calculator.
Value decoding → use a calculator.
See other components: